验证迁移安全性
本部分描述的修改可以在支持的代码仓库中的 PR #8 找到。
验证迁移安全性
由于数据库是我们应用程序的关键组件,我们希望在修改它时不会破坏任何事情。 不良的规划迁移会导致数据丢失、应用程序停机和其他问题。 Atlas 提供了确认迁移可以安全运行的机制。 这种机制称之为 迁移静态检查(migration linting), 在本部分我们将会展示如何使用它来验证迁移是安全运行的。
静态检查迁移目录
我们可以使用 atlas migrate lint 命令来静态检查迁移目录。
为演示这一点看我们看一下如果我们将 User 模型中的 Title 字段由可选改为必须会发生什么:
// Fields of the User.
func (User) Fields() []ent.Field {
return []ent.Field{
field.String("name"),
field.String("email").
Unique(),
-- field.String("title").
-- Optional(),
++ field.String("title"),
}
}
让我们重新运行代码生成:
go generate ./...
下一步让我们自动生成一个新的迁移:
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- PostgreSQL
- SQLite
atlas migrate diff user_title_required \
--dir "file://ent/migrate/migrations" \
--to "ent://ent/schema" \
--dev-url "docker://mysql/8/ent"
atlas migrate diff user_title_required \
--dir "file://ent/migrate/migrations" \
--to "ent://ent/schema" \
--dev-url "docker://mariadb/latest/test"
atlas migrate diff user_title_required \
--dir "file://ent/migrate/migrations" \
--to "ent://ent/schema" \
--dev-url "docker://postgres/15/test?search_path=public"
atlas migrate diff user_title_required \
--dir "file://ent/migrate/migrations" \
--to "ent://ent/schema" \
--dev-url "sqlite://file?mode=memory&_fk=1"
一个新的迁移文件在 ent/migrate/migrations 目录中被创建了:
-- modify "users" table
ALTER TABLE `users` MODIFY COLUMN `title` varchar(255) NOT NULL;
现在让我们静态分析此迁移目录:
atlas migrate lint --dev-url mysql://root:pass@localhost:3306/dev --dir file://ent/migrate/migrations --latest 1
Atlas 报告此次迁移可能运行起来是不安全的:
20221116051710_user_title_required.sql: data dependent changes detected:
L2: Modifying nullable column "title" to non-nullable might fail in case it contains NULL values
Atlas 检测到迁移运行起来不是安全的并阻止我们运行它。 这种情况下 Atlas 将此处变更分类为数据依赖变更。 这意味着变更可能失败,且取决于数据库中的某些数据。
Atlas 可以检测更多其他类型的问题,完整列表参见 Atlas 文档。
在 CI 中静态分析迁移目录
在上一部分我们看到了如何本地静态检查迁移目录。 在本部分我们将了解在 CI 中如何静态检查迁移目录。 通过这种方法我们可以确认在我们合并迁移到主分支之前迁移历史在可以安全运行。
GitHub Actions 是 GitHub 推出的流行的 CI/CD 产品。 通过 GitHub Actions 用户可以简单地定义工作流,工作流可以在 Git 代码仓库相关的多种生命周期事件中触发。 例如许多团队配置 GitHub Actions 在每次提交变更到代码仓库时运行全部的单元测试。
GitHub Actions 一个非常强大的功能是它的扩展性:可以轻松将功能片段打包成模块(称为 “action”)并在之后许多项目中重复使用。
使用 GitHub 的团队希望确保所有数据库模式的变更都是安全的话,可以使用 atlas-action GitHub Action。
这个动作(action)使用 atlas migrate lint 命令完成 静态检查迁移目录。
这个命令验证并分析迁移目录内容并为选中的变更生成洞察与诊断:
- 确保迁移历史记录可从任意时间点进行回放。
- 当多个团队成员同时向迁移目录写入迁移操作时,防止意外的历史变更。
- 检测是否已发生破坏性或不可逆的变更,或这些变更是否依赖于数据表内容从而可能导致迁移失败。
使用
添加 .github/workflows/atlas-ci.yaml 到代码仓库并写入如下内容:
name: Atlas CI
on:
# Run whenever code is changed in the master branch,
# change this to your root branch.
push:
branches:
- master
pull_request:
paths:
- 'ent/migrate/migrations/*'
jobs:
lint:
services:
# Spin up a mysql:8.0.29 container to be used as the dev-database for analysis.
mysql:
image: mysql:8.0.29
env:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: pass
MYSQL_DATABASE: dev
ports:
- "3306:3306"
options: >-
--health-cmd "mysqladmin ping -ppass"
--health-interval 10s
--health-start-period 10s
--health-timeout 5s
--health-retries 10
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3.0.1
with:
fetch-depth: 0 # Mandatory unless "latest" is set below.
- uses: ariga/atlas-action@v0
with:
dir: ent/migrate/migrations
dev-url: mysql://root:pass@localhost:3306/dev
现在无论合适我们拉取可能存在不安全性的迁移,Atlas GitHub Action 都会运行并报告静态检查结果。 例如数据依赖变更:
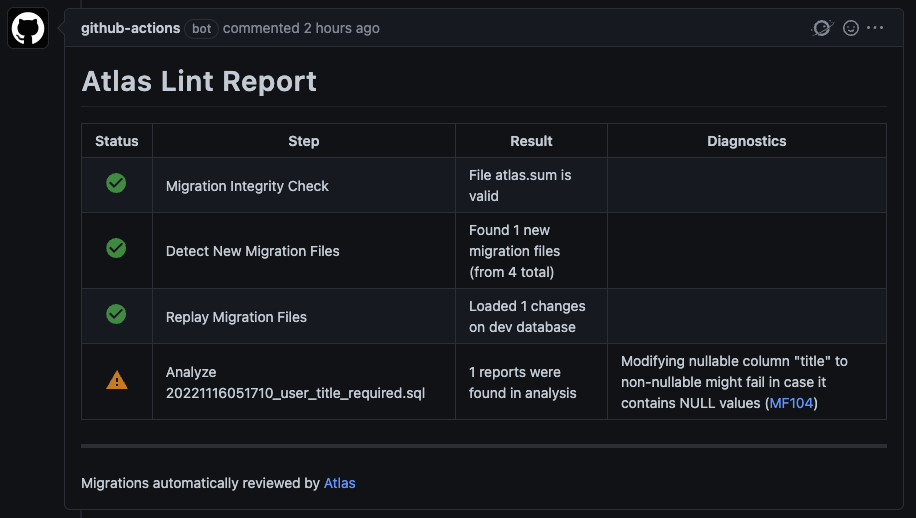
更深入的文档请参见 Atlas 网站的文章 atlas-action。
让我们回填 title 列来解决这个问题。在迁移文件添加如下语句:
-- modify "users" table
UPDATE `users` SET `title` = "" WHERE `title` IS NULL;
ALTER TABLE `users` MODIFY COLUMN `title` varchar(255) NOT NULL;
重新对迁移目录进行哈希计算:
atlas migrate hash --dir file://ent/migrate/migrations
重新运行 atlas migrate lint,我们可以看到迁移目录此时已经没有任何不安全的变更了:
atlas migrate lint --dev-url mysql://root:pass@localhost:3306/dev --dir file://ent/migrate/migrations --latest 1
因为没有找到任何问题,命令会以零值退出并不作任何输出。
当我们将此变更提交到 GitHub,Atlas GitHub Action 会运行并报告此问题已经解决:

总结
在本部分我们了解了如何使用 Atlas 通过本地运行和在 CI 中运行来确认迁移是安全的。
我们的教程如何升级 Ent 项目由自动化迁移到版本化迁移就至此结束了。 简而言之我们学会了如何:
- 开启版本化迁移功能标志
- 基于期望的 Ent 模式创建脚本进行自动规划迁移
- 升级生产环境数据库使用 Atlas 版本化迁移
- 规划项目自定义迁移
- 使用
atlas migrate lint确认迁移的安全性
后续
- 订阅我们的 Newsletter
- 关注我们的 Twitter
- 加入 #ent 频道:Gophers Slack
- 加入我们: Ent Discord Server